Former Project on Planetary Agenda
OES – 沖縄科学技術大学院大学(OIST)でのプラットフォームの構築
コミュニティ向け自律型DCマイクログリッド(DCOES)
DCオープンエネルギーシステム(DCOES)は全く新しいタイプのボトムアップ式電力融通網です。コミュニティ内の個々の住宅が発電し、住宅と住宅の間でエネルギーを相互融通する、従来とは異なる電力網です。既存の電力系統に影響を及ぼすことなく、エネルギーの需給バランスを自律的に調整することで、エネルギー自給率を高めることができます。沖縄において、19戸の住宅をDC電力線で結び自律相互融通の実証実験を行っています。
DCOES Implementation
実施方法
各住宅に蓄電池、太陽光パネルなどから成る蓄電システムが設置されており、各蓄電システムを専用のDC電力線(バス)と通信線によって相互接続することでDCマイクログリッドを形成します。DCマイクログリッド内の個々の住宅間で、ピアツーピアの電力融通を行います。
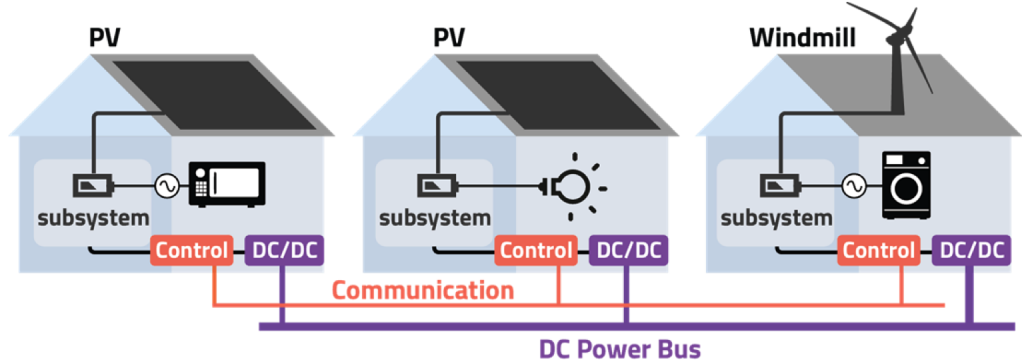
図1:DCオープンエネルギーシステムの構造
DCオープンエネルギーシステム(DCOES)では、分散された発電源からの電力をDCマイクログリッドにより相互接続させたボトムアップ式を採ることにより接続を動的に変更することができます。これにより、需要やコミュニティの大きさなどに柔軟に対応することが可能で、既存の送電網では考えられなかったような柔軟性のある電力網を構築することができます。そして、自律分散型電力制御ソフトウェアによって、様々なシナリオに合うように住宅間の電力融通が制御されます。
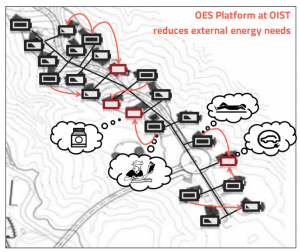
図2:利用パターンに合わせて電力融通を自律的に制御する
これまで一世紀以上にわたって、電力システムにはAC(交流)が使われてきました。ACはDCに比べ、電圧変換が容易であるものの、エネルギーの統合が難しいという特徴がありました。ところが近年高効率のDCDCコンバータが開発され、DCでの電圧変換が容易になりました。また、蓄電池、太陽光パネルおよびほとんどの家電製品はDCで動作しています。私たちは、マイクログリッドにおいてもDCを使用することで効率的な電力融通を実現しています。
沖縄のOESプラットフォーム
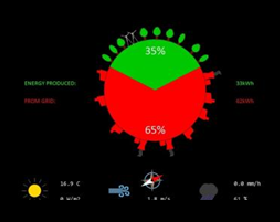
現在、沖縄のプラットフォームでDCOESのコンセプトの実証実験を行っています。19戸の住宅のそれぞれに太陽光パネル、リチウムイオン蓄電池を設置しそれらを自営DC電力線で接続しています。2015年2月2日から2日間にわたって開催された第2回オープンエネルギーシステム国際シンポジウムでは、全19戸間での自律型電力融通のデモンストレーションを行いました。そこではリアルタイムで発電・蓄電・電力融通をモニタリングすることができます。
※本実証実験は沖縄県“亜熱帯・島しょ型エネルギー基盤技術研究補助事業”の採択を受け、㈱沖創工、ソニービジネスオペレーションズ㈱、沖縄科学技術大学院大学(OIST)との共同研究体で実施中です。
 図3:沖縄で実施されているオープンエネルギーシステムの実証実験
図3:沖縄で実施されているオープンエネルギーシステムの実証実験
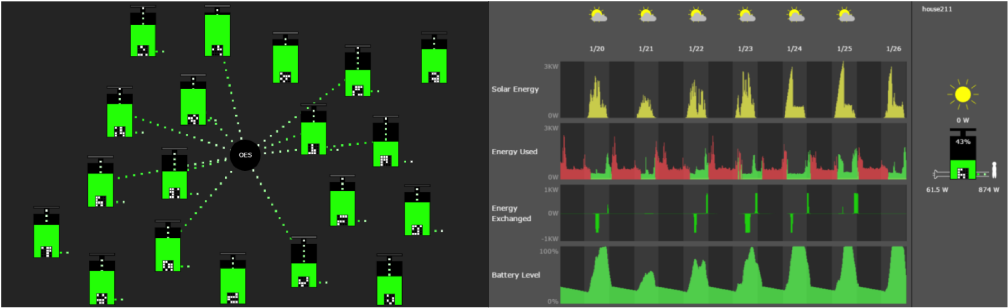
図4:沖縄のシステム
DCOES-OIST20 Autonomous Energy Exchange Visualization
Keywords
Related News
同じリサーチエリアの別プロジェクト
Creativity
モジュラー式電力システム及び電力フローの可視化
アートを紡ぐサイエンス
創造、エンターテインメント、センスオフワンダーを広げる