国際宇宙ステーションと地上間で高速信号処理装置の軌道上実証に成功
株式会社ソニーコンピュータサイエンス研究所(代表取締役社長:北野宏明 以下、ソニーCSL)は、国際宇宙ステーション(ISS)の「きぼう」日本実験棟に設置された光通信アンテナ(以下、QSOL:Quantum-Small Optical Link)と国立研究開発法人情報通信研究機構(以下、NICT)の宇宙光通信地上局(以下、光地上局)※1との間で光通信リンクを確立し、ギガビットイーサネットによる動画データのダウンリンクに成功しました。伝送方式にはソニーCSL独自開発規格の自由空間光イーサネット通信用誤り訂正技術※2を用いています。なお、この規格で行われた通信は世界初となります。
QSOLは、総務省からの委託を受けNICT、次世代宇宙システム技術研究組合(NeSTRA)、国立大学法人東京大学、スカパーJSAT株式会社とソニーCSLが軌道上技術実証のために共同開発した、小型衛星光通信システム「SeCRETS(SECuRE lasEr communicaTionS terminal for Low Earth Orbit)」の光通信アンテナ部分となります。SeCRETS は2023年8月2日に国際宇宙ステーションへ向けて打ち上げられ、「きぼう」日本実験棟の船外実験プラットフォーム(中型曝露実験アダプター(i-SEEP))に設置されました。その後、低軌道上のISSから地上の可搬型光地上局への10GHzクロックの光通信により秘密鍵共有を実施し、さらにその鍵を用いたワンタイムパッド暗号によりISSと地上局とでの情報理論的に安全な通信の実証に成功しました※3。
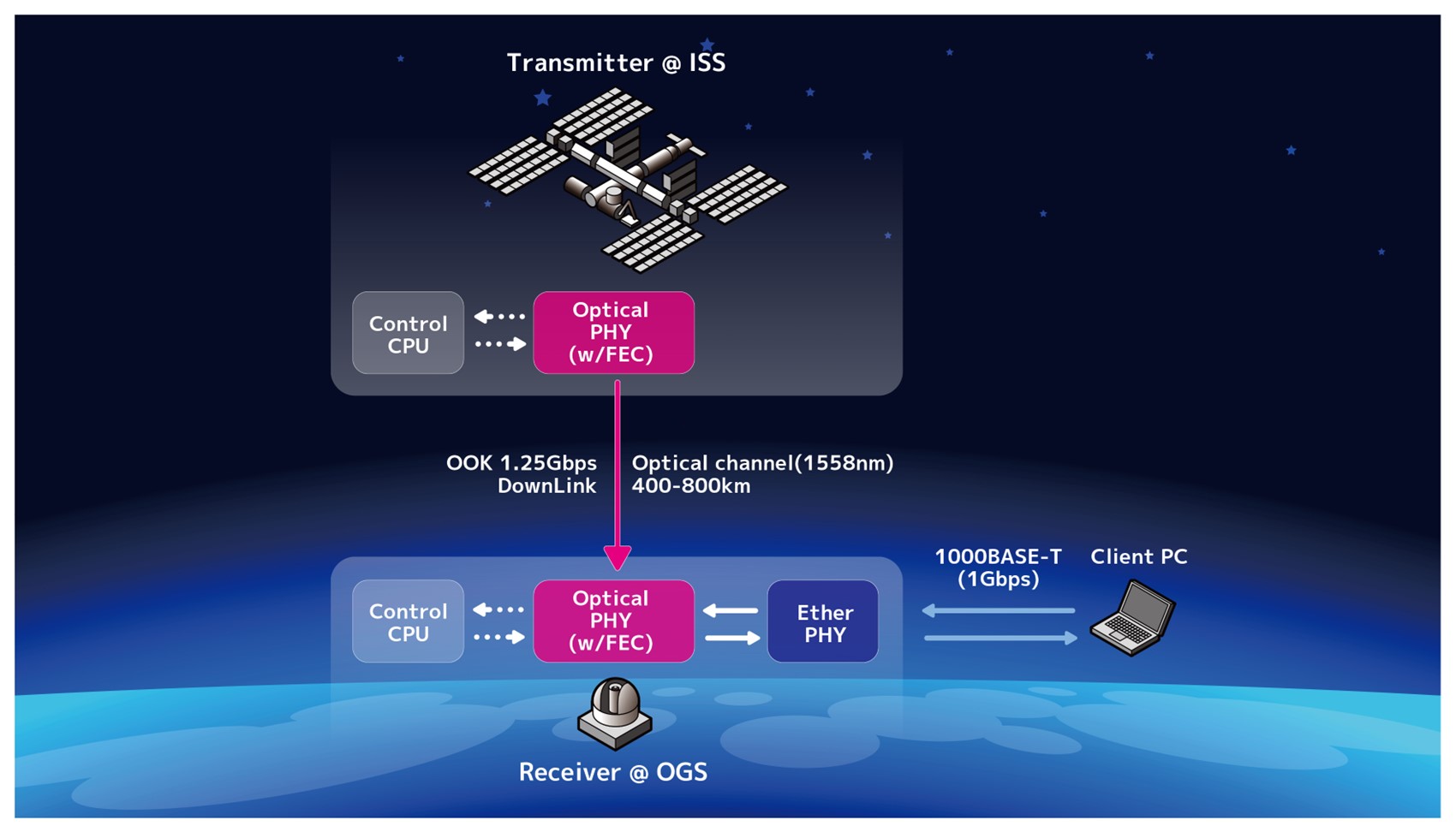
今回の実験の概念図
QSOLは、地上に設置された光地上局を捕捉追尾するためのジンバル機構や、光地上局に通信光を送信する精追尾光学系、及びそれらの制御装置に加え、1.25 Gbpsの高速光通信を実証するための信号処理装置等から構成されています。
今回の実験では、QSOLの潜望鏡型小型ジンバルシステムを使用してNICTの可搬型光地上局からアップリンクしたビーコン光を捕捉追尾し、上記可搬型光地上局、およびNICTの1.5m光地上局に向けてダウンリンク光を出射し、光通信リンクを確立させるという光アンテナの軌道上実証に成功しました。さらに、動画データをQSOLが送信するビーコン光に乗せて軌道上からダウンリンクし、NICTの1.5m光地上局にて受信することにも成功しました。これには、ソニーCSLが開発した自由空間光イーサネット通信用誤り訂正技術が使用されています。
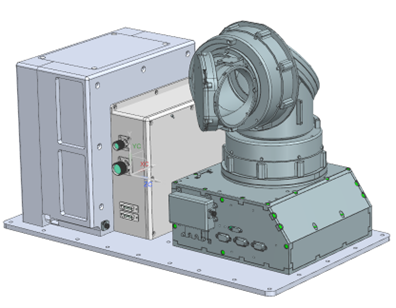
QSOL構成図
ソニーCSLは2020年に小型衛星搭載用の光通信機器でEthernetによる通信を世界で初めて実現し、精細度(HD)画像データの伝送に成功しています。その後、2021年には世界初の商用光地上局までの光ダウンリンク確立にも成功しました。
そして、今回の実験では動画ファイルの伝送を達成しました。この取り組みにより、宇宙と地上間での堅牢性のあるデータ通信機能や、小型、広視野範囲を実現するジンバルシステム機能、小口径の光アンテナ(可搬型光地上局)との光リンクを実現する精追尾機能等が宇宙空間で十分に発揮できることを確認しました。ソニーCSLは、宇宙と地上間での本格商用通信の実現に向けた重要な成果と捉えており、今後の宇宙空間における通信の社会実装が期待されます。
※1NICT光地上局
宇宙通信に係わる技術を開発するために設置された望遠鏡施設。東京都小金井市に口径1.5m、1.0m、茨城県鹿嶋市に口径1.0m、沖縄県国頭郡恩納村に口径1.0mの計4基の望遠鏡が設置されている。今回の実験では口径1.5mの望遠鏡を使用した。
※2宇宙データシステム諮問委員会(CCSDS)の予備検討規格
(142.10-O-1 REED-SOLOMON PRODUCT CODE FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION
https://www.sonycsl.co.jp/tokyo/15743/
※3国際宇宙ステーションと地上間での秘密鍵共有と高秘匿通信に成功 “衛星量子暗号通信の実用化に期待”
https://www.sonycsl.co.jp/press/prs20240418/
(2024/4/18 プレスリリース)
本研究開発は、総務省「ICT重点技術の研究開発プロジェクト(JPMI00316)」のうち「衛星通信における量子暗号技術の研究開発(JPJ007462)」の一環として実施されました。
(参考)総務省報道発表
2018年6月14日付け
平成30年度 情報通信技術の研究開発に係る提案の公募の結果
http://www.soumu.go.jp/menu_news/s-news/01tsushin03_02000247.html
株式会社ソニーコンピュータサイエンス研究所 広報窓口
csl-pr@csl.sony.co.jp
in Orbit with Transmission
between International Space Station and Ground
Sony Computer Science Laboratories, Inc. (Sony CSL, President and CEO: Hiroaki Kitano) has successfully downlinked video data via gigabit Ethernet from the Quantum Small Optical Link (QSOL) installed aboard the Japanese Experiment Module “Kibo” on the International Space Station (ISS) to the optical ground station for satellite communications (hereinafter, optical ground station)1 of the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT). The transmission was made using Sony CSL’s free-space optical Ethernet communications error-correction technology, an independently developed standard.2 This marks the first use in the world of this standard to make a transmission.
QSOL is the optical antenna component of the compact Secure Laser Communications Terminal for Low Earth Orbit (SeCRETS). It was commissioned by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications to demonstrate the technology in orbit and was jointly developed by NICT, Next generation Space system Technology Research Association (NeSTRA), The University of Tokyo, SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation, and Sony CSL. SeCRETS was launched on August 2, 2023, to the ISS and installed to the IVA-replaceable Small Exposed Experiment Platform (i-SEEP) on the outside of “Kibo”. Subsequently, experiments of 10 GHz clock optical transmission between the ISS in low Earth orbit and a portable optical ground station were successfully conducted to share private keys and to demonstrate information-theoretically secure transmission of one-time pad encryption.3

Conceptual diagram of the experiment
QSOL is composed of an optical transmission signal processing unit for demonstrating 1.25 Gbps high-speed transfer and contains a gimbal for acquisition and tracking of the optical ground station, an optical bench with fine pointing system, and a control system.

Structure of QSOL
For this experiment, QSOL’s compact periscope gimbal system tracked and acquired an uplink from NICT’s portable optical ground station and then downlinked to their 1.5 m optical ground station. An optical link was established, demonstrating the use of QSOL in orbit. Additionally, video data was downlinked from QSOL in orbit and received by NICT’s 1.5 m optical ground station. This transmission used the free-space optical Ethernet communications error-correction technology developed by Sony CSL.
In 2020, Sony CSL transmitted high-definition (HD) image data via Ethernet, marking the first time in the world that a successful link was established using laser communication devices designed for small satellites. Later, in 2021, Sony CSL achieved the first successful downlink at a commercial optical ground station.
This time, a video data file was successfully transmitted. Through this, Sony CSL has thoroughly demonstrated robust data transmission between space and ground, a compact gimbal system with large field of view, and the tracking and acquisition of a small aperture optical antenna (portable optical ground station) to establish an optical link. Sony CSL considers this result a significant step toward realizing commercial transmission between space and ground, and foresees great potential in its social implementation in the future.
1 NICT Optical Ground Station
A telescope facility built to aid the development of technology related to space communications. The station has a total of four telescopes with apertures of 1.5 m and 1.0 m in Koganei, Tokyo; 1.0 m in Kashima, Ibaraki; and 1.0 m in Onna, Kunigami-gun, Okinawa. The experiment this time used the telescope with a 1.5 m aperture.
2 142.10-O-1 Reed-Solomon Product Code for Optical Communication, an experimental
specification (orange book) of the Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS).
3 Successful private key sharing and high confidentiality communications between the International Space Station and the ground ~ Expectations for practical satellite quantum cryptography communications ~
https://www.sonycsl.co.jp/press/prs20240418/
(18 Apr 2024, press release, Japanese only)
This research and development was carried out as part of the “Research and Development of Quantum Cryptography in Satellite Communications (JPJ007462)” within the “Research and Development Project for Priority ICT Technologies (JPMI00316)” of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications.
Reference: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications press release
Dated 14 June 2018.
Results of the call for proposals for research and development of information and communication technologies in 2018.
http://www.soumu.go.jp/menu_news/s-news/01tsushin03_02000247.html
Corporate Communications, Sony Computer Science Laboratories, Inc.
csl-pr@csl.sony.co.jp