(電力融通制御ソフトウェア)無償提供を開始
~ 地産地消型の再生可能エネルギー導入を促進し、サステイナブル社会の実現へ ~
株式会社ソニーコンピュータサイエンス研究所(代表取締役社長:北野宏明 以下、ソニーCSL)は、独自開発のP2P(ピアツーピア)電力融通技術を活用したマイクログリッドシステム「Open Energy System™(以下、OES)」の中核モジュールである電力融通制御ソフトウェア「Autonomous Power Interchange System(以下、APIS)」をオープンソース化し、2020年12月1日より無償提供を開始します。
近年、気候変動問題は深刻さを増しており、一日も早く再生可能エネルギーへの大規模かつ合理的な転換が求められます。再生可能エネルギーの導入形態は多様ですが、ソニーCSLは、分散型で拡張可能性が高く、さらに災害等に対するレジリエンス(強じん性)で優れているマイクログリッドという電力システムの研究開発を進めてきました。マイクログリッドは、太陽光発電などの再生可能エネルギーを始めとする分散電源を活用することで、温室効果ガス排出量を抑制するとともに、一定の地域で使用する電力を地域内で発電、蓄電、配電することで、送配電距離を最小化し、自然災害等の障害の影響を最小化できます。
ソニーCSLでは、マイクログリッドシステムOES関連技術をアフリカや沖縄などで実証試験してきました。特に、沖縄科学技術大学院大学(OIST)においては、教職員住宅群に対して5年間にわたり電力供給を行い、この技術の安定性と有用性を確認しました。ソニーCSLのミッションは、「人類の未来のための研究」を行うことであり、そのミッションの実現のために研究成果をベストな方法で展開することは我々の責務です。このような認識のもとで、気候変動という人類規模の問題に貢献するために、独自に開発を続けてきた電力融通制御ソフトウェアAPISをオープンソース化することとしました。オープンソース化することにより、様々なステークホルダーが一体となった取り組みの活性化や大学等における再生エネルギー関連研究の加速、マイクログリッド関連スタートアップの出現など、様々なオープンイノベーションが推進されるものと考えています。そして、ソニーCSLがこの技術を占有した場合より、遥かに迅速かつ大規模な導入の可能性が高まると期待しています。
<OES及びAPISの開発背景>
現在一般的なAC(交流電源)マイクログリッドは、その安定化を石油やガスを熱源とするコージェネレーションなどに依存しているケースが多く、CO2排出をゼロにできません。また、十分な蓄電設備を有しない場合には、太陽光発電などによる急激な発電量の変動に対応する交流発電装置の制御に制限があるなどの要因(いわゆる逆潮流問題)で再生可能エネルギーの導入量に限界があるなど、環境面での課題があります。
OESは、DC(直流電源)を基盤としたマイクログリッドを構成する技術体系であり、太陽光発電などの分散発電源と分散蓄電装置を直流グリッドでつなぐことによりこれらの問題を克服しています。APISはその中核となる自律的に電力融通制御を実現するソフトウエアであり、以下の三つの特長を有します。
- 柔軟なグリッド拡張:自律的な電力融通が可能となることで、システムの再設計を行わずにマイクログリッドの柔軟な拡張が可能となります。
- 再エネ有効利用:分散発電源と蓄電装置間の電力融通が可能となることで、発電量の変動が想定される再生可能エネルギーを有効に利用することが可能となります。
- レジリエンス:また、これらの機能が実現されることで、レジリエンス性が高い電力システムの構築が可能となります。
一方で、OESのようなDCマイクログリッド技術は、その優位性が議論されるものの、そのシステム開発や制御に関する公開情報は少なく、実用レベルでの研究開発や新規事業者が参入するために活用可能な技術やツールが少ない状況にありました。これらの課題を解決すべく、自律動作可能なバッテリーシステムを分散設置し、バッテリーシステムを相互に接続する、独自のバッテリ分散型DC(直流電源)マイクログリッドOES、およびその制御ソフトウェアAPISを開発するに至りました。
<APISの機能>
今回オープンソースで提供するソフトウェアAPISは分散設置されたバッテリー間のP2P電力融通により、再生可能エネルギーを主電源とした運用を可能とするマイクログリッドを構築でき、電力システムのレジリエンスを高めます。コミュニティ内の個々の住宅や設備の需要や、再生可能エネルギーに特長的な発電量の増減に対しても柔軟に電力を自動融通し、コミュニティ内の需給バランスを調整することで、電力自給率向上にも寄与します。
◆PC上でマイクログリッド内の電力融通をエミュレーションする機能
APISを用いることで、マイクログリッド導入の検討にあたり、様々なパラメーターにおける電力融通の動作検証を行えます。
◆マイクログリッドを構築するバッテリーシステムを制御する機能
APISと各バッテリーシステムに対応したデバイスドライバを準備することで、様々なハードウェアに対応する柔軟性の高いマイクログリッドを構築できます。
<APISを活用したマイクログリッドの特長>
- 分散バッテリーの協調制御により、薄く分散して時間的な変動が大きい再生可能エネルギーの利用効率を向上する。
- 2台のバッテリーシステムから導入可能で、後から容易かつ柔軟にシステムを拡張可能なスケーラビリティ。
- マイクログリッドに障害が発生しても最低限の動作を継続する事が可能なシステム構成。
- リモートモニタリングによる障害の自動通知により、システムの運用が容易となる。
- 停電した際に、外部電力に頼ることなく発電を開始できる「ブラックスタート」が容易となる。
- 大規模な発電所がなく、送電網が整備されていない場所などでも地域内で電気を有効に活用、共有可能となる。
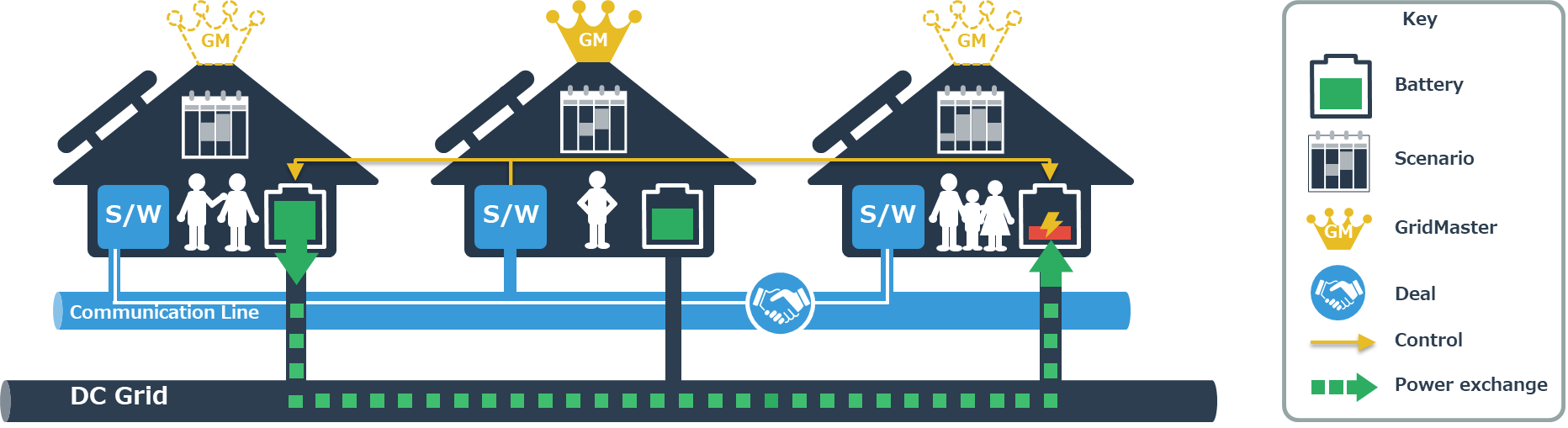
電力を融通し合う自律分散協調制御のイメージ
<導入事例>
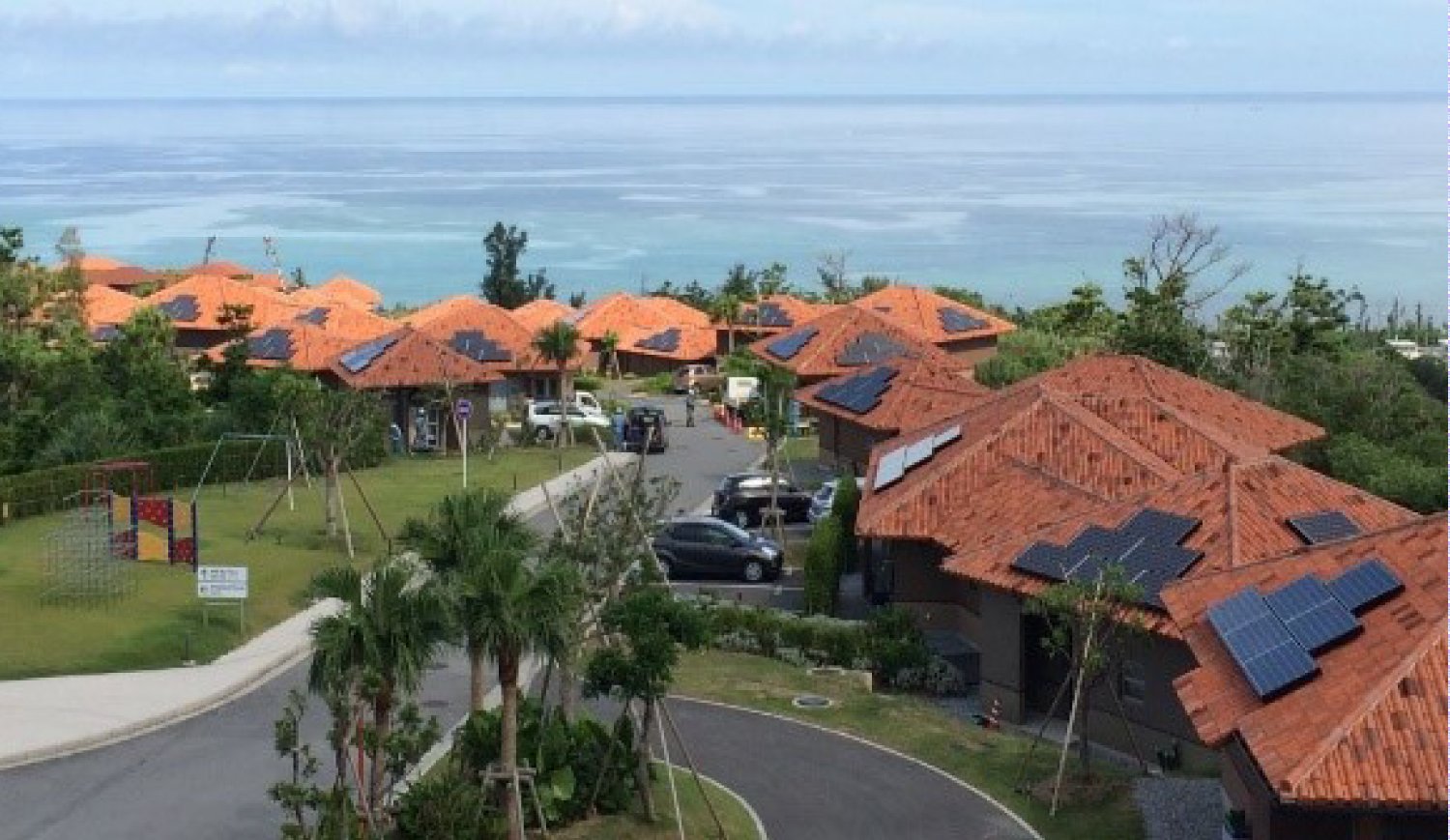
沖縄科学技術大学院大学 (OIST) にある19戸の教員用住宅に設置された太陽光パネルとバッテリーシステムにはAPISの技術を活用したエネルギーシステムが搭載されており、2014年12月より継続して稼働してきました。このOISTのエネルギーシステムでは、電気設備点検におけるAC電力供給停止時においても、約10時間にわたり継続的な電力供給を実現しています。また、電力供給の1日最大60.8%、年間平均33.3%を再生可能エネルギーで供給しています。(※2017年:ソニーCSL測定データより)
これらの教員用住宅では、従来の電力系統とOESの連動を検証する目的もあり、設備容量を1戸あたりPV(Photovoltaic) 3.5kW、バッテリー4.8kWhに設定し、全電力需要の3割から6割をOESで供給する設計としていますが、この設備容量を増強することで、より高い再生可能エネルギー導入量の実現も可能となります。(シミュレーション上では、PV 10.0kW、バッテリー15.0kWhの設備容量で年間93%を再生可能エネルギーで供給可能)(本実証実験は沖縄県“亜熱帯・島しょ型エネルギー基盤技術研究補助事業”の採択を受け、沖縄科学技術大学院大学(OIST)、株式会社沖創工、ソニービジネスオペレーションズ株式会社との共同事業体で実施しました。)
 |
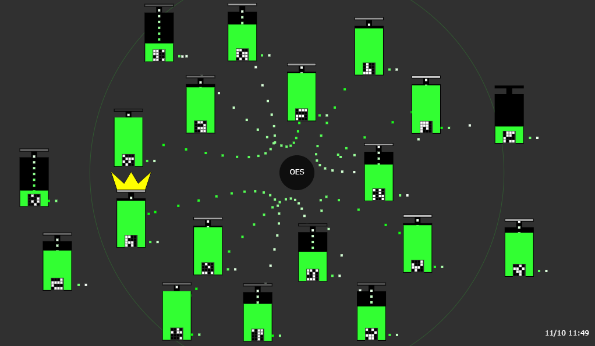 |
OISTで稼働しているシステム |
各住宅のリアルタイムバッテリーモニタリング状況 |
<ソニーCSL代表取締役社長 北野宏明のコメント>
『ソニーCSL、人類の未来のための研究を行うというミッションを遂行するために、OESのみならず、協生農法や低軌道衛星通信網などの研究とその実用化などを推進しています。地球環境の問題は、単に二酸化炭素濃度の問題だけではなく、生物学的多様性をいかに維持増大させるか、生活の質を維持向上させながら資源要求を劇的に減少させることが技術的に可能か、さらには、それを現実のものとする社会変革をいかに達成するかという大きな課題を抱えています。特に、気候変動は、Climate Departureといわれる不可逆的気候遷移が引き起こされるリスクを前提に対策を講じる必要があります。そのためには、OESに見られるような再生可能エネルギーシステムの迅速かつ広範な導入により、環境への影響を低減するとともに、変動する環境下においても安定的なエネルギー供給を実現することが重要です。この度の OES/APISのオープンソース化を通じて、より多くのステークホールダーとともに、持続可能な社会の実現に貢献していくことを目指したいと思います。』
Open Energy System(OES)
URL:https://www.sonycsl.co.jp/sp/287/
Autonomous Power Interchange System(APIS)
URL:https://www.sonycsl.co.jp/tokyo/11481/
株式会社ソニーコンピュータサイエンス研究所 広報窓口 csl-pr@csl.sony.co.jp
(Power-interchange Management Software)Going Open Source
Promote locally produced & consumed renewable energy,
work towards a sustainable society
On December 1, 2020, Sony Computer Science Laboratories, Inc. (Sony CSL; President & CEO: Hiroaki Kitano) will make its Autonomous Power Interchange System (APIS)—the power-interchange management software that comprises the core module of microgrid Open Energy System™ (OES) and the proprietary peer-to-peer (P2P) power interchange technology they develop open source, meaning it will be freely available to the public.
In recent years, climate change has become ever more serious, demanding that we undertake a practicable, large-scale shift from fossil fuel energy to renewable energy—every day counts. The adoption of renewable energy can take many forms, but Sony CSL has undertaken research and development of electric power systems known as microgrids, which are decentralized, highly scalable, and exceptionally resilient to natural disasters. A microgrid utilizes decentralized, renewable energy sources, including solar and others, to generate, stores and distributes power for use by a specific area while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This is a highly resilient power system that minimizes the transmission and distribution distance from generation to consumption, which eventually reduces the impact of physical damage wrought by natural disasters.
Sony CSL has done pilot projects of microgrid OES related technologies in locations including Africa and Okinawa, Japan. At the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST), we have provided power to faculty housing units for five years, confirming that our technology is both stable and practical. Sony CSL’s mission is to “carry out research for the future of humanity,” and if we are to fulfill that mission, it is our responsibility to deliver research results using the best methods available to us.
This is why we have made our independently developed Autonomous Power Interchange System (APIS) software open source: to help tackle climate change, an issue that impacts all humankind. We believe that making this technology open source will promote all sorts of open innovation, energizing a variety of stakeholders to come together, accelerating research into transformation towards renewable energy at universities and scientific institutes, and spurring the emergence of microgrid-related startups. Thus, we expect that the adoption of this technology is likely to occur much more rapidly and widely than if it were in the sole possession of Sony CSL.
OES & APIS Development Background Currently, most conventional alternating current (AC) microgrids rely on cogeneration that uses oil or gas as a stabilizing energy source, which means CO2 emissions will never reach zero. Also, without sufficient battery capacity, there are limits to how much renewable energy you can bring in, which in turn is due to the limits of how flexibly AC generators can respond to the sudden fluctuations of solar energy and other renewables(i.e. the reverse power flow problem). These are just some of the practical problems at play. Open Energy System (OES) technology overcomes these problems with direct current (DC) microgrids. Decentralized power generators using solar and other renewables and decentralized power storage equipment are directly connected within the grid. The Autonomous Power Interchange System (APIS) is the software that acts as the “core module” to make this technology possible. It has three distinguishing features.
- Flexible grid expansion: Because power interchange is autonomous, the microgrid can be expanded flexibly, without having to redesign the system from the ground up.
- Effective use of renewables: Because the power interchange occurs between decentralized power generators and decentralized power storage equipment, it is possible to use renewable energy effectively despite fluctuations in the amount of power generated.
- Resilience: Because of these characteristics, it is possible to build a power system with high resilience.
Although the merits of OES-style DC microgrid technology are often discussed, the fact is that very little information is out there about how these systems are developed and managed, and how they could be implemented in R&D projects or used by entrepreneurs. In order to change that, we developed our proprietary OES decentralized-battery direct current (DC) microgrid—which includes decentralized battery systems that can work autonomously in concert with the grid—and the APIS software to manage it.
APIS Functionality Through P2P power interchange between decentralized batteries, the APIS software that we are now making open source allows for the creation of microgrids that operate primarily on renewable energy and offer a power system with increased resilience. This system can perform power interchange autonomously and flexibly, responding to the needs of individual residences and facilities within a community, and to the characteristic fluctuations of renewable energy. The balance of supply and demand within the community is carefully regulated, leading to greater energy independence.
◆Emulation of Microgrid Power Interchange on a PC
If you are considering the adoption of microgrid technology, with APIS you can perform operation verification of power interchange under various parameters.
◆Control of a Microgrid’s Battery Systems
By setting up APIS together with device drivers for each battery, you can build a flexible microgrid system that works with various types of hardware.
Features of an APIS Microgrid
- Improve use efficiency of renewable energy sources (which are thinly distributed and highly variable over time) due to coordinated control of decentralized batteries.
- Scalability. Start with as few as two batteries, and flexibly and easily expand the system from there.
- A system that can continue emergency operations even in the event of microgrid failure.
- Remote monitoring that offers automatic notification of any failure, making system operations easier.
- After a power outage, easy to do a “black start”—restoring power without relying on an external power source.
- Effective utilization and sharing of power within a given region, even in areas with no large power plant or reliable power grid.

Autonomous, decentralized & coordinated control of power interchange
Pilot Project
At the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST), 19 faculty residences have had energy systems—featuring solar panels and batteries and utilizing APIS technology—installed and operational since December 2014. This OIST energy system successfully provides approximately 10 hours of continuous power, even when the regular AC power supply is shut down for inspection. Furthermore, it provides up to 60.8% of daily power supply, and an annual average of 33.3% of total power supply comes from renewables. (Sony CSL measurements from 2017)
In this faculty housing project, our aim was to verify that a conventional power system and OES could work in concert. The capacity for each home was set at 3.5kW of photovoltaic (PV) cells, and a 4.8kWh battery, meaning OES would meet between 30% and 60% of the total power demand. However, by strengthening this capacity, it would be possible to achieve a greater share for renewable energy. (According to our simulations, PV10.0kW + battery 15.0kWh capacity would mean 93% of power coming from renewable energy) (This project was supported by the “Subtropical and Island Energy Infrastructure Technology Research Subsidy Program,” Okinawa Prefectural Government. Also, the test is being held in collaboration with Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST), Okisokou、Ltd., and Sony Business Operations,Inc.)
 |
 |
System in operation at OIST |
Realtime battery monitoring of each residence |
Comment from Hiroaki Kitano, Sony CSL President & CEO “Sony CSL’s mission is to carry out research for the future of humanity. In order to fulfill that mission our efforts are not limited to OES.We are also undertaking research and implementation of projects ranging from Synecoculture™ farming to low earth orbit optical communications networks. The environmental challenges we are facing are not just about concentrations of carbon dioxide. We must also ask: How can we sustain or even increase biodiversity? Is there a technology that will allow us to dramatically reduce our demand for resources, while sustaining or improving our current living standards? How will we achieve the societal changes needed to successfully tackle these challenges? In particular, when it comes to climate change, we need to take actions which proceed on the assumption that we are already in danger of “Climate Departure”, where the climate undergoes irreversible change. With this in mind, it is vital that we are able to provide stable supplies of power in unstable environments through the swift and widespread adoption of renewable energy systems such as the ones we see in OES. By making OES/APIS open source, we hope to increase the number of stakeholders in this project and contribute to the realization of a sustainable society.”
Open Energy System(OES)
URL:https://www.sonycsl.co.jp/sp/287/
Autonomous Power Interchange System(APIS)
URL:https://www.sonycsl.co.jp/tokyo/11481/
csl-pr@csl.sony.co.jp